The so-called annual shaping pruning refers to shaping and trimming performed according to different requirements throughout the year. By pruning and pruning to cultivate a good tree skeleton, coordinate the relationship between growth and results, improve the scenery conditions, and achieve the purpose of high quality and high yield for successive years. According to the characteristics of the Red Fuji apple, the pruning should be based on the principle of using small crowns as the main body, pruning for the four seasons as a means, and combining the results with the long trees. Summing up the experience and lessons learned from the production practice of Qixia Apple over the years, the planting density of Red Fuji is 34 meters, and the tree shape is the most suitable for the free spindle shape. First, free-spindle-shaped tree structure The trunk height is 60-80 cm, the height of the tree is about 3 meters, and the crown diameter is about 2.5 meters. There is a strong center, where a main branch is planted every 15-20 centimeters, and the whole tree has 12-15 main branches, arranged in a spiral. The main branch with the same direction should be maintained at more than 60 cm. The main branch directly bears the result branch group, maintains the uniaxial extension, the main branch angle should be maintained at about 80 degrees, and the base thickness should not exceed 1/3 of the center dry thickness of the implantation site, emphasizing the master-slave separation. Second, the young tree shaping pruning technology The young apple trees refer to the trees before the three-year-old. The main task of this period of pruning is to cultivate the tree shape, and strive to basically complete the selection and retention of each backbone branch within three years and build a good skeleton of the tree. (A) Pruning in the first year after colonization 1. Make it dry. At an even height of full shoots, cut approximately 100 cm in height. 2. Summer trim. From mid-May to the end of May, when the lateral shoots reach about 20 cm in length, they can be picked up and the competition branches can be picked up at 10 cm to maintain the absolute advantage of central shoot growth. (b) Pruning for the second year after colonization 1. Winter trimming. First, choose a branch that stands upright and grows more prosperous as the central leadership branch, and cut about 100 centimeters around the full bud. For the rest of the annual branch at the main branch position, heavy short cuts or 2-3 axillary shoots or shearing shears (cut into horseshoe shapes) can be applied depending on the situation; positional discomfort is completely removed from the base. 2. Spring pruning. In late March or early April, starting from the seventh bud under the central leadership branch, one bud was carved every six buds until the height of the trunk to prepare for the emergence of the backbone. 3. Summer trim. For the competition branches and early picking of the heart, in addition to the need to select branches other than the backbone sticks, the denser ones are removed and the others are picked up at the right time. 4. Autumn trim. In August and September, the competition branches and the useless branches were removed. In addition to the central leadership, the rest of the branches are all open to about 80. (c) Pruning for the third year after colonization 1. Winter trimming. The selection and retention of the central leadership branch was the same as the previous year. The rest of the main branches and the auxiliary branch of the main branch were all put slowly and not cut (some weak main branches could be cut at full shoots). 2. Spring pruning, mainly sprouting. The standard of budding is: the central leadership is the same as the previous year. The slow release of the main branch and the rest of the branches are three or five minutes away. On both sides and behind the buds, the axillary buds must be slightly heavier, about 25 cm shorter, and the base not more than 20 cm. . 3. Summer pruning: (1) Sparse inside the crown without uselessness and peripheral shoots; (2) Competitive shoots and main shoots on the back of the main branch; pruning or short cuts; (3) Slow-cut shoots in the spring in late May Strong and weak, girdling or circumcision at the base of 10 cm. Do not circumcise the trunk. 4. Autumn pruning: basically the same as in the previous year, such as the occurrence of upright and vigorous sparse shoots on the back of the main branch. Three, early fruit apple tree pruning The early fruit trees refer to the trees before the five or six years of life. The main task of tree pruning in this period is to successfully complete the selection and retention of the branches and branches on the basis of pre-shaping, and to pay attention to alleviating the tree potential; The proportion of short branches, coordinate the relationship between growth and results; vigorously cultivate the results of the branches, under the premise of ensuring the quality of fruit, the rapid increase in yield, so that fruit trees in time into the full fruit period. (a) winter pruning 1. Pruning of central leadership branches: If the number of main branch selections in the early period is not enough, the cutting can be continued depending on the specific situation. When the number of main branches has been selected enough, it can be put slowly and not cut, after the slow release, the summer ring cuts and the autumn pulls are carried out. . 2. Pruning of main branches and auxiliary branches: Extension branches are still placed in slow release; peripheral branches and strong branches on the back can be removed. 3. Result of the cultivation of the branch group: It is obtained by cultivating the continuation method and the contraction method. The continuous release method refers to the slow release of the successive years. The deflation method means that when the tree vigor is weak or the space is small, it is appropriate when the tree is released slowly for several years. Retracted parts. (b) Spring pruning: 1. According to the standard carved buds of all kinds of branches, the length of branches within 30 cm do not need to bud. 2. When the flowering amount of the tree is large, the weak flower buds can be removed after the flower buds are sprouted, or the flower buds of the long fruiting buds in some parts can be removed, especially the peripheral flower buds of the stem branches. 3. For some strong branches with small flowers, carry out circumcision during the flower bud red period to improve the fruit setting rate. (c) summer trim 1. The main branch back to Wang tipping or cutting. 2. Weed out new shoots and new shoots from outside. 3. Proper circumcision is performed on branches with few results and strong growth. (four) autumn trim 1. Continue to open all kinds of branches. 2. Remove stub branches and back strong branches and dense branches. Benzyl Carbazate CAS No. 5331-43-1 Benzyl Carbazate Basic Information
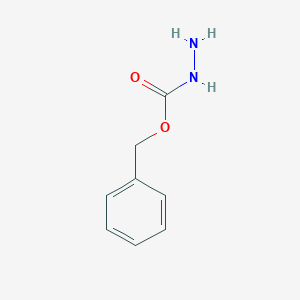
Benzyl Carbazate Structure
Benzyl carbazate Chemical Properties
benzyl carbazate,benzyl carbamate msds,benzyl carbazate synthesis,benzyl carbamate solubility,benzyl carbazate wikipedia,Benzyl hydrazinecarboxylate ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com
CAS: 5331-43-1
MF: C8H10N2O2
MW: 166.18
EINECS: 226-230-3
Product Categories: Phosgene Derivatives
Mol File: 5331-43-1.mol
Boiling point 294.38°C (rough estimate)
density 1.2265 (rough estimate)
storage temp. 2-8°C
Water Solubility Soluble in water (slightly), methanol and DMSO.
Red Fuji Apple Anniversary Shaping Technique
